- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2024-04-30 Origin: Site








Magnesium oxide board, often abbreviated as MgO board, stands as a versatile and innovative material in modern construction practices. Composed primarily of magnesium oxide, it boasts a unique composition that distinguishes it from conventional building materials. This sturdy yet lightweight board is formed through a process involving magnesium oxide, magnesium chloride, perlite, and wood chips or sawdust. Its composition renders it highly resistant to fire, moisture, mold, and insects, making it an ideal choice for a variety of construction applications. As safety concerns continue to be at the forefront of building design and implementation, understanding the intrinsic safety features of materials like magnesium oxide board becomes paramount. Incorporating materials with robust safety characteristics not only ensures the protection of structures and occupants but also aligns with regulatory standards and promotes sustainable building practices. Thus, exploring the definition, composition, and safety considerations surrounding magnesium oxide board unveils its significance as a reliable and indispensable component in the realm of modern construction. The manufacturing process of magnesium oxide board involves a meticulous series of steps to produce a durable and versatile construction material. Beginning with the selection of raw materials, manufacturers carefully source components such as magnesium oxide, magnesium chloride, perlite, and wood chips or sawdust. These ingredients are combined in precise proportions to form a homogeneous mixture, ensuring uniformity and consistency in the final product. Production methods and techniques vary but commonly include mixing the raw materials with water to form a slurry, which is then poured into molds and compressed under high pressure. This process helps to remove excess moisture and bind the ingredients together, forming solid boards. Throughout production, stringent quality control measures are implemented to monitor the composition, density, and strength of the boards. Regular testing and inspection procedures ensure that each batch meets rigorous standards for fire resistance, moisture resistance, and structural integrity. By understanding the intricacies of the manufacturing process, one can appreciate the meticulous attention to detail and craftsmanship involved in creating magnesium oxide board—a reliable and indispensable material in modern construction. magnesium oxide, it boasts a unique composition that distinguishes it from conventional building materials. This sturdy yet lightweight board is formed through a process involving magnesium oxide, magnesium chloride, perlite, and wood chips or sawdust. Its composition renders it highly resistant to fire, moisture, mold, and insects, making it an ideal choice for a variety of construction applications. As safety concerns continue to be at the forefront of building design and implementation, understanding the intrinsic safety features of materials like magnesium oxide board becomes paramount. Incorporating materials with robust safety characteristics not only ensures the protection of structures and occupants but also aligns with regulatory standards and promotes sustainable building practices. Thus, exploring the definition, composition, and safety considerations surrounding magnesium oxide board unveils its significance as a reliable and indispensable component in the realm of modern construction. Fire resistance: Explanation of its non-combustible properties Moisture resistance: Prevention of water damage and mold growth Durability: Longevity and resistance to wear and tear Sustainability: Environmental advantages compared to traditional materials Cost-effectiveness: Analysis of long-term savings Magnesium oxide board, renowned for its versatility and reliability, finds extensive application across various sectors of the construction industry, catering to diverse needs and requirements. As a staple in modern construction, magnesium oxide board serves as a prime choice for interior walls and ceilings in both residential and commercial buildings. Its lightweight yet robust nature makes it easy to handle and install, providing a sturdy foundation for interior spaces while offering acoustic insulation properties. Additionally, magnesium oxide board excels as exterior cladding, offering superior protection against weather elements such as rain, wind, and UV radiation. Its resistance to moisture and fire ensures long-lasting performance, enhancing the durability and aesthetics of building exteriors. Moreover, magnesium oxide board proves its mettle in subflooring applications, delivering unmatched strength and stability for flooring installations. Its ability to withstand heavy loads and resist moisture makes it an ideal choice for high-traffic areas in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Furthermore, magnesium oxide board is a preferred option for fire-rated assemblies, as its non-combustible properties ensure compliance with stringent building codes and regulations. Lastly, its versatility extends to specialty applications, including hospitals, schools, and industrial settings, where stringent safety and hygiene standards are paramount. By harnessing the diverse applications of magnesium oxide board, construction professionals can create resilient, sustainable, and aesthetically pleasing structures that meet the evolving demands of the built environment. Getting Started with Magnesium Oxide Board: What It's Made of and Why Safety Counts?
Manufacturing Process of MGO Board
Benefits of Using Magnesium Oxide Board
Applications in Construction

Magnesium oxide is a natural non-toxic inorganic mineral. It is calcined and pulverized into powders and mixed in the magnesium chloride solution.
Magnesium chloride (MgCl2) is added to the magnesium oxide powder to create an aqueous solution. It is stirred until it becomes cement slurry.
Perlite (PO4) is a type of obsidian, which is a vitric rock cooled rapidly from lava in volcanic eruption. It is widely used as an insulating material and added to magnesium oxide boards to enhance its fire resistance.
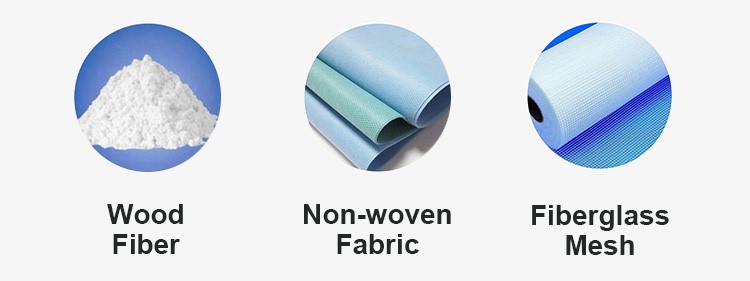
Wood fiber, also known as sawdust, is mixed into the cement slurry and acts as an adhesive to assist the overall performance of the product.
Non-woven fabric is composed of directional or random fibres, with moisture-proof, breathable, flexible and other characteristics.
Fiberglass mesh is an inorganic non-metallic material with excellent performance, which increases the strength and toughness in the board.
Magnesium oxide board, renowned for its versatility and reliability, finds extensive application across various sectors of the construction industry, catering to diverse needs and requirements. As a staple in modern construction, magnesium oxide board serves as a prime choice for interior walls and ceilings in both residential and commercial buildings. Its lightweight yet robust nature makes it easy to handle and install, providing a sturdy foundation for interior spaces while offering acoustic insulation properties.
Additionally, magnesium oxide board excels as exterior cladding, offering superior protection against weather elements such as rain, wind, and UV radiation. Its resistance to moisture and fire ensures long-lasting performance, enhancing the durability and aesthetics of building exteriors. Moreover, magnesium oxide board proves its mettle in subflooring applications, delivering unmatched strength and stability for flooring installations. Its ability to withstand heavy loads and resist moisture makes it an ideal choice for high-traffic areas in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Furthermore, magnesium oxide board is a preferred option for fire-rated assemblies, as its non-combustible properties ensure compliance with stringent building codes and regulations. Lastly, its versatility extends to specialty applications, including hospitals, schools, and industrial settings, where stringent safety and hygiene standards are paramount. By harnessing the diverse applications of magnesium oxide board, construction professionals can create resilient, sustainable, and aesthetically pleasing structures that meet the evolving demands of the built environment.